Electric Scaffolding Lifts: The Complete Guide to Operation, Applications, and Safety
Electric scaffolding lifts represent a significant advancement in construction and maintenance technology, offering enhanced efficiency and safety for workers who need to access elevated work areas. These motorized platforms have transformed how teams approach vertical projects, reducing physical strain while improving productivity. As industries continue to prioritize worker safety and operational efficiency, understanding the capabilities, applications, and safety features of electric scaffold lifts becomes increasingly important.
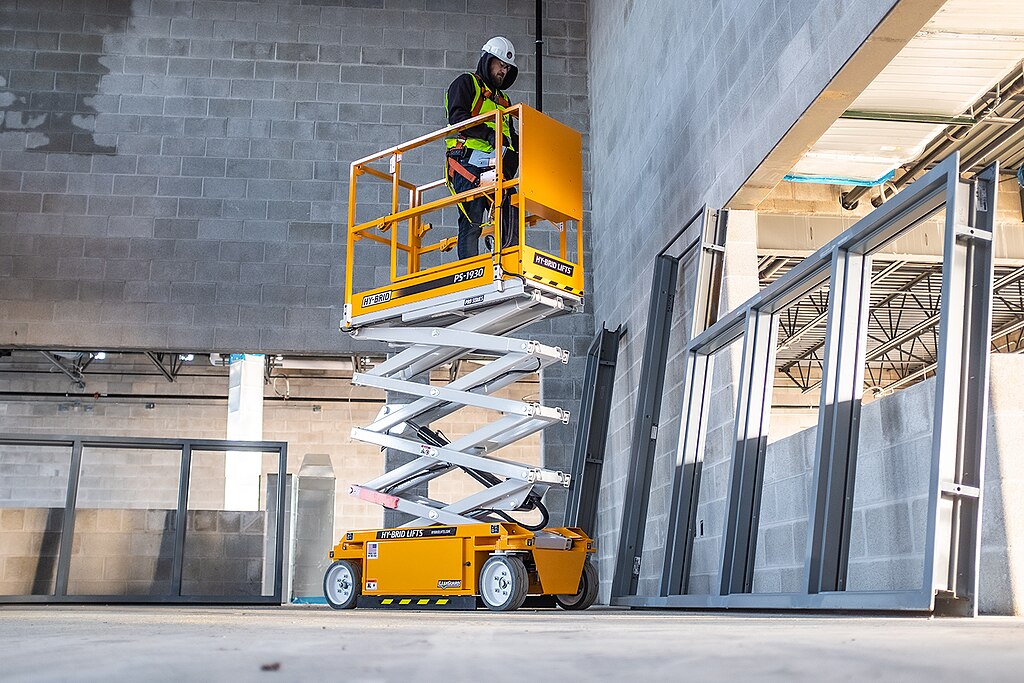

What to Know About Electric Scaffolding Lifts and How They Work
Electric scaffolding lifts operate on a relatively straightforward principle. They consist of a work platform mounted on a vertical mast or series of extendable sections powered by an electric motor. The motor drives a rack and pinion system, chain mechanism, or hydraulic cylinders that enable the platform to move vertically along the mast structure. Most modern electric scaffold lifts operate on rechargeable battery systems, though some models can be plugged directly into power sources.
The control systems of electric scaffold lifts typically feature intuitive interfaces with up/down buttons, emergency stop functions, and may include additional capabilities like self-leveling mechanisms for uneven terrain. Many contemporary models incorporate electronic sensors that prevent operation if weight limits are exceeded or if the lift isn’t properly stabilized. These intelligent systems ensure the lift remains within safe operating parameters.
One of the significant advantages of electric scaffold lifts is their smooth, controlled movement. Unlike manual alternatives that require physical effort to raise and lower, electric models provide consistent motion without jerking or sudden drops, making them ideal for tasks requiring precision or when transporting delicate materials.
Where Electric Scaffold Lifts Are Commonly Used in Construction and Maintenance
Electric scaffold lifts have found widespread applications across numerous industries. In commercial construction, they’re invaluable for interior finishing work like ceiling installation, HVAC servicing, electrical wiring, and painting. Their compact footprint and maneuverability make them particularly well-suited for confined spaces where traditional scaffolding would be cumbersome to erect.
In industrial settings, electric scaffold lifts facilitate maintenance work on large equipment, production lines, and warehouse infrastructure. Manufacturing facilities utilize these lifts for accessing overhead equipment, performing routine inspections, and conducting repairs without disrupting floor operations. Their clean electric operation produces no emissions, making them appropriate for indoor use even in sensitive environments.
Maintenance teams responsible for large buildings rely heavily on electric scaffold lifts for tasks such as window cleaning, façade maintenance, lighting replacement, and HVAC servicing. Theatrical and event production companies also employ these lifts for installing lighting, sound equipment, and decorative elements. Additionally, retail environments use compact electric scaffold lifts for inventory management and display installation in high-ceilinged spaces.
The versatility of electric scaffold lifts has made them indispensable in environments where frequent height changes are necessary or where work needs to be performed at multiple elevations throughout the day. Rather than repeatedly disassembling and rebuilding traditional scaffolding, workers can simply reposition the electric lift as needed.
How Electric Models Compare to Manual or Hydraulic Lifts
When evaluating scaffold lift options, understanding the differences between electric, manual, and hydraulic systems helps determine the most appropriate choice for specific applications. Electric scaffold lifts offer several advantages over their counterparts, particularly in terms of ease of use and operational efficiency. Unlike manual lifts that require physical exertion to raise platforms through hand cranks or winch systems, electric models eliminate operator fatigue during vertical movement.
Compared to hydraulic lifts, which rely on fluid pressure systems, electric lifts generally require less maintenance as they have fewer potential leak points and don’t need regular fluid checks or replacements. Electric models also tend to provide more precise height control and smoother operation than basic hydraulic systems. However, hydraulic lifts often excel in environments with extremely heavy loads or where explosive/flammable conditions might make electric motors problematic.
From an environmental perspective, electric scaffold lifts produce zero emissions during operation, making them ideal for indoor use or environmentally sensitive areas. In contrast, hydraulic systems with combustion engines generate exhaust and noise pollution. Electric models typically have lower long-term operating costs due to their energy efficiency, though their initial purchase price may be higher than manual alternatives.
The primary limitations of electric scaffold lifts include their dependence on battery life or power sources, potential charging downtime, and typically lower maximum load capacities compared to some heavy-duty hydraulic systems. For projects requiring extended operation periods without access to charging facilities, hydraulic or manual systems might be more practical options.
Key Safety Features and Load Capacities Often Found in Scaffold Lifts
Safety remains paramount when operating scaffold lifts, and modern electric models incorporate numerous protective features. Most electric scaffold lifts include automatic braking systems that engage immediately when power is cut or if the lift experiences unexpected movement. Outriggers and stabilizers enhance stability by creating a wider base, preventing tipping even when the platform is fully extended.
Overload sensors have become standard on quality electric scaffold lifts, automatically preventing operation if the platform weight exceeds safe limits. These systems often incorporate visual or audible warnings to alert operators before critical thresholds are reached. Guardrails, toe boards, and self-closing gates provide physical protection against falls, while emergency descent mechanisms allow for controlled lowering of the platform during power failures.
Regarding load capacity, electric scaffold lifts typically range from 300-1,000 pounds (136-454 kg) for standard models, though specialized industrial versions may accommodate significantly more weight. When evaluating capacity requirements, it’s crucial to consider not only the workers’ weight but also tools, materials, and equipment that will be used on the platform. Many manufacturers specify separate values for indoor versus outdoor use, with reduced capacities for outdoor operations due to wind load considerations.
Most electric scaffold lifts for construction and maintenance applications offer working heights between 15-50 feet (4.5-15 meters), with compact models designed for interior work typically providing lower maximum heights but enhanced maneuverability. Platform sizes generally range from 24-36 inches (61-91 cm) wide and 3-8 feet (0.9-2.4 meters) long, depending on the intended application and required capacity.
When selecting an electric scaffold lift, organizations should conduct thorough risk assessments of their specific applications and ensure operators receive proper training on equipment features, limitations, and emergency procedures. Regular inspection and maintenance programs remain essential for ensuring continued safe operation throughout the equipment’s service life.